Intel’s Flagship Processor Lunar Lake Boasts Enhanced Efficiency for Thin Laptops
Intel has announced its new flagship solution, Lunar Lake, for thin laptops. This processor incorporates the newly developed P-cores Lion Cove and E-cores Skymont. The latter shows significant improvements compared to its predecessor, nearly doubling the performance of previous similar-class cores used in Meteor Lake.
Improved Cores Promises Enhanced Performance
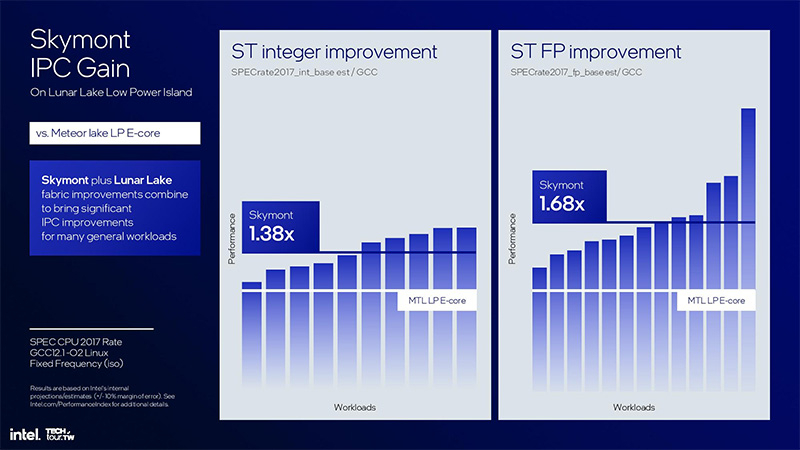
The Lion Cove P-cores have seen considerable microarchitectural advancements. However, the Skymont E-cores stand out even with these upgrades. Compared to the previous generation E-cores, Crestmont, used in Meteor Lake, the integer tasks IPC (Instructions per Cycle) surged by 38%, and the floating-point algorithms saw an increase of 68%. Apart from this, Intel has also doubled the Skymont’s performance in vector loads, which use AVX- and VNNI-instructions.
Revamped Architecture for Greater Efficiency
The Lunar Lake E-core features major architectural enhancements, such as broader mechanisms for decoding and out-of-order execution, extended pipeline, amplified number of executive devices, and a doubled combined 4 MB second-level cache with improved throughput.

Performance Advantage
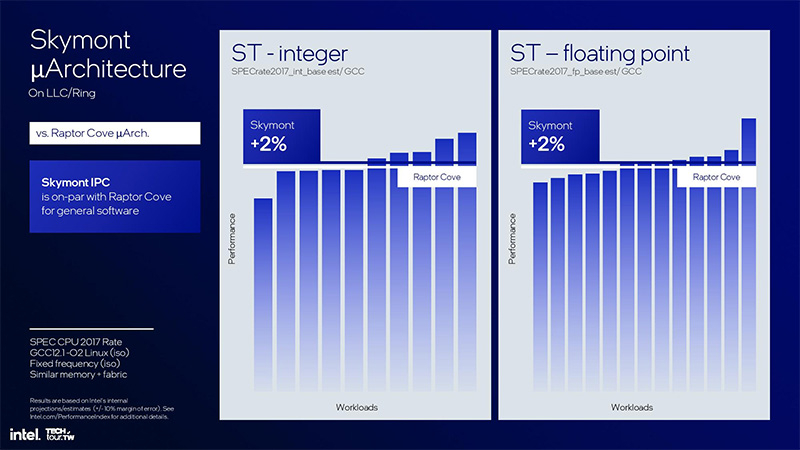
As stated by Intel, the new Skymont E-cores can provide nearly double the performance advantage compared to the low-voltage E-cores of Meteor Lake. Interestingly, the new Skymont E-cores, when clocked at the same frequency, are on average 2% more efficient than the Raptor Cove P-cores used in Raptor Lake processors, both in integer and floating-point loads.
Improved Distribution Strategy
The Skymont architecture is Intel’s third variation of the E-core after Alder Lake’s Gracemont and Meteor Lake’s Crestmont. The Lunar Lake processors will incorporate one four-core Skymont cluster. Earlier, Meteor Lake’s design included a pair of additional low-voltage E-cores, which has been abandoned in Lunar Lake to eliminate energy consumption differentiation between the E-cores.
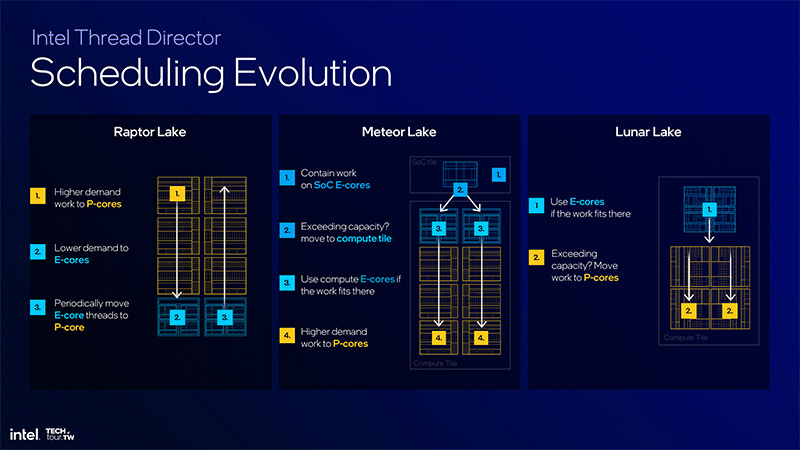
In light of the significant progress in E-core performance, Lunar Lake processors will utilize an updated Thread Director dispatcher to enhance load distribution efficiency across P- and E-cores. The notable change is a new load distribution strategy. Initially, all threads will be sent to the E-cores, and only when the E-cores are overloaded or their performance is inadequate for the task at hand, the load will be shifted to the more efficient P-cores. According to Intel, this strategy provides significant energy savings in typical office applications.
Availability
The Lunar Lake processors with Skymont-E cores are set to be released in the third quarter of 2024. They will be utilized in thin laptops on the Intel platform that meet the Copilot Plus PC requirements. Later in the year, Arrow Lake processors, intended for desktop PCs, will be released. They will also employ the efficient Skymont cores.





