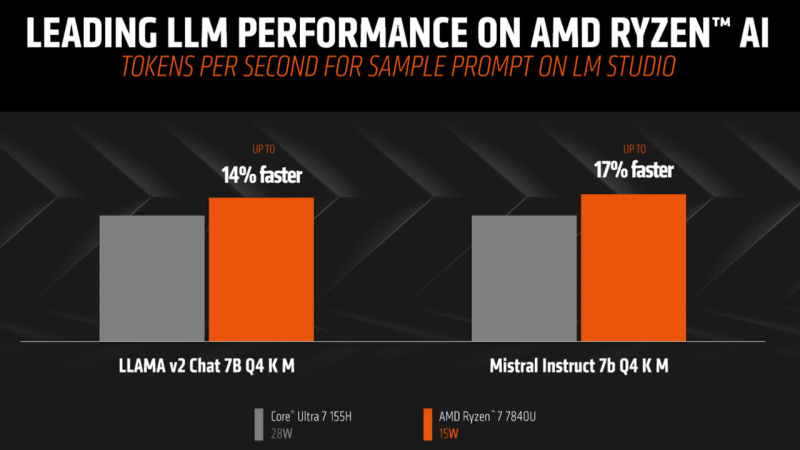
In-house testing conducted by AMD indicates that its mobile processor, the Ryzen 7 7840U, outperformed competitor Intel Core Ultra 7 155H in artificial intelligence (AI) performance. This is despite the AMD processor’s lower power consumption of 15W compared to the Intel processor’s 28W thermal design power (TDP), when working with large language models (LLM) Llama 2 and Mistral Instruct 7B.
Testing Methodology
The comparison involved AMD installing the LM Studio application on laptops equipped with each of the competing processors. The AI models were tasked with writing a story, a script for a Unity-engine game, and a poem using the Llama 2 7B, a product of Meta, and the 7 billion parameter-supported Mistral Instruct 7B, developed by Meta alumni and DeepMind.

Key Performance Indicators
AMD used ‘Time to First Token’ and ‘Number of Tokens Issued per Second’ as AI performance indicators. The Ryzen processors have three core types: the specialized AI-engine NPU, the built-in RDNA 3 graphics core, and the Zen 4 processing cores for tackling AI tasks. AMD credited the Ryzen 7 7840U’s superior performance to its support for AVX512 and VNNI instructions, a feature previously supported by Intel but later discontinued.
Outstanding Performace of AMD
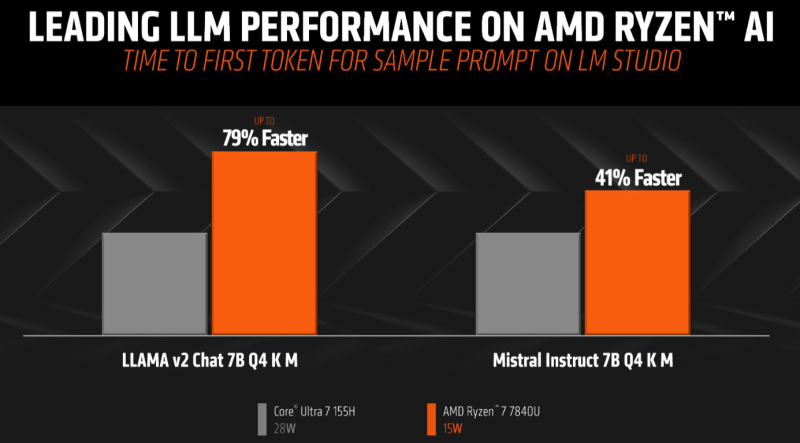
Running LM Studio
In addition to the testing results, AMD also published a comprehensive guide in their official blog on how to run the LM Studio tool for using LLM on Ryzen AI processors or Radeon RX 7000 GPUs.
Intel’s Road Ahead
According to tech site Tom’s Hardware, Intel is well aware of the relatively low AI performance of its Meteor Lake processor family. Consequently, they have stated that the future Arrow Lake and Lunar Lake processors, expected to be released later this year, will offer triple the AI performance for GPUs and NPUs.





