The Internet is home to an enormous wealth of data, with hundreds of billions of web pages indexed. While one might perceive the online world to continue expanding over time, this isn’t entirely accurate. New research from the Pew Research Center vividly displays the transient nature of web content.
Web Page Availability Over Time
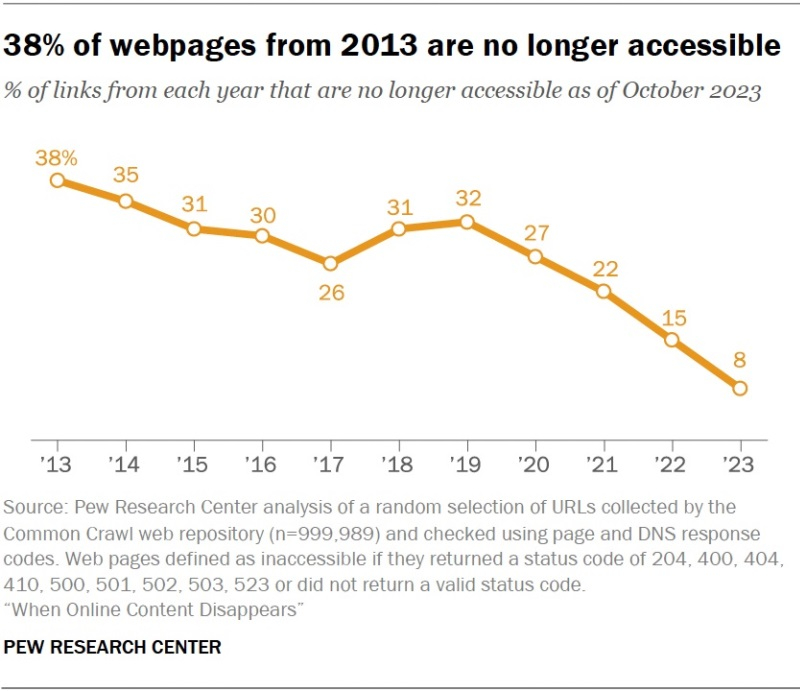
Analysts have calculated that a quarter of all web pages in existence from 2013 through 2023 are already unavailable as of October 2023. Most often, this results from radical changes or deletions over time. This trend is also true for older content. About 38% of web pages from 2013 are currently unavailable, and of those existing in 2023, 8% are presently inaccessible.
Broken Links: A Prevalent Issue
Specialists from the Pew Research Center studied links appearing on government, news websites, and Wikipedia’s “References” section in the spring of the same year. The analysis revealed that 23% of news web pages and 21% of government web pages contain at least one non-functioning link. Broken links are especially common on sites for local authorities or city administrations, with 54% of Wikipedia pages listing at least one URL to a nonexistent page.
Social Media Pages
To trace the disappearance of social media pages, analysts collected tweets from platform X in spring 2023 and monitored them over three months. Almost every fifth post became unavailable a few months after publication. In 60% of cases, the account posting the tweet became private, suspended, or was deleted from the platform within the same period. In the remaining 40% of cases, the account owner removed the tweet, but the account persisted. Notably, over 40% of tweets in Turkish or Arabic disappear from the site within three months of publication.
Last Decade’s Web Pages
For this part of the analysis, experts gathered a random sample of almost 1 million web pages from the Common Crawl archives. Analysts selected pages from each year starting in 2013 (approximately 90,000 pages per year), checking for current availability. By October 2023, 25% of the collected web pages were already inaccessible, with 16% representing uniquely inaccessible pages on functioning sites, and 9% due to the site’s discontinuation. Unsurprisingly, most of the unavailable resources are from older archives, with 38% of the pages from 2013 ceased functioning by October 2023.
Government Website Links
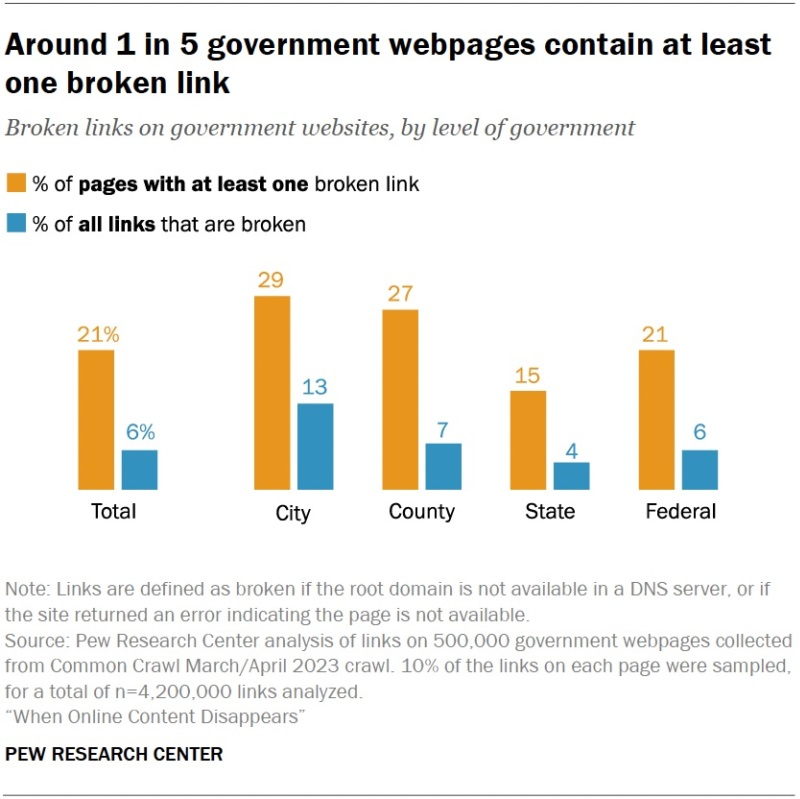
Approximately 500,000 pages from government websites were selected from the Common Crawl archive for March-April 2023 for this segment of the analysis. In total, these pages hosted 42 million links (86% internal links). Roughly three-quarters of web pages from the selection contained at least one link, with an average of 50 links per page. Overall, 21% of studied pages on government websites contained at least one broken link.
News Portal Links
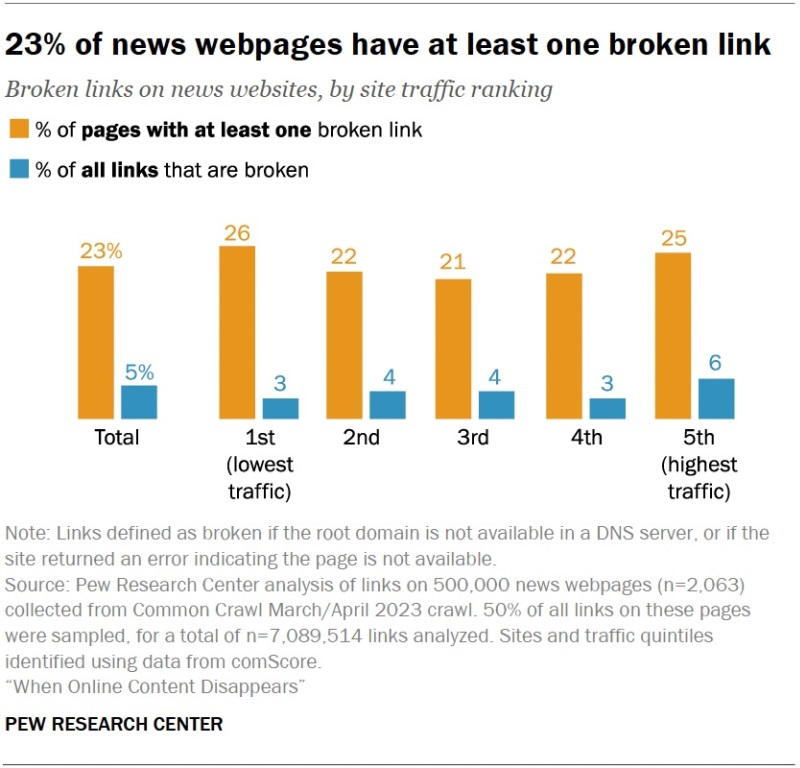
This category analyzed 500,000 pages from 2,063 websites classified as “News and Information” by comScore. The pages were collected from the Common Crawl archive for March-April 2023. In total, the selected pages contained 14 million links (an average of 20 links per page), with 5% of all links no longer working and 23% of pages containing at least one link to a nonexistent resource. Approximately 25% of pages from the top 20 most visited news websites hosted at least one broken link.
Reference Links on Wikipedia
Analysts selected 50,000 English Wikipedia pages and studied the links contained in the “References” section. Around 82% of pages hosted at least one broken external link, with more than 1 million links across all pages from the selection, 11% of which are now unreachable.
Social Media X Posts
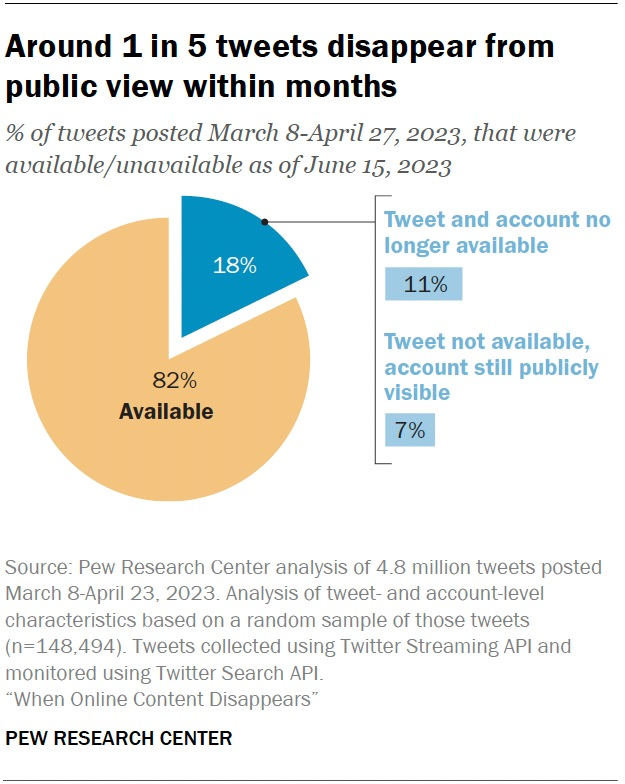
The study included 5 million tweets posted from March 8 to April 27, 2023, on social media X, then known as Twitter. Researchers then followed these posts until June 15 of the same year, checking their availability daily. By the end of the study, 18% of the original tweets were no longer viewable on the platform, principally because the author’s account was either blocked or entirely deleted. The majority of tweets are deleted from X within a month. Specifically, 1% of posts disappear within an hour after posting, 3% within a day, 10% within a week, and 15% within a month. In other words, about half of tweets that disappear from the platform become unavailable within the first six days, and 90% of such tweets vanish within 46 days.





