AMD’s Latest Ryzen 8000G Chips Exhibit Lower Performance
During CES 2024, AMD only provided sparse technical information about its latest desktop hybrid processors, the Ryzen 8000G series. However, new details have surfaced, suggesting some Ryzen 8000G chips aren’t up to par with their counterparts.
Differences in AMD Ryzen 8000G Series
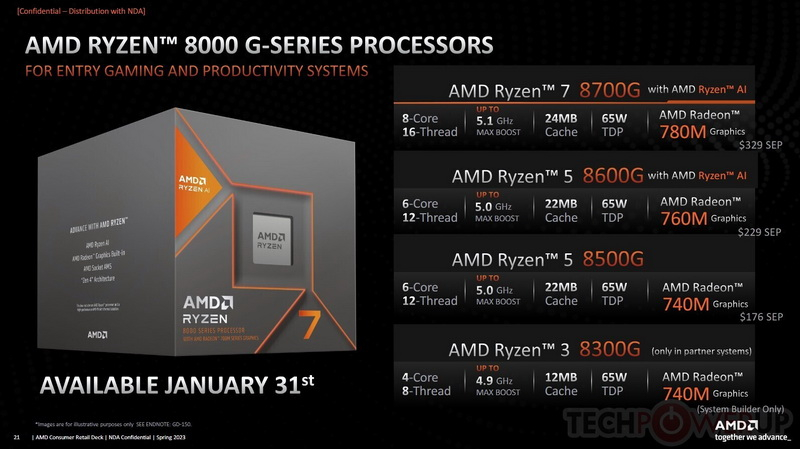
AMD uses two distinct types of crystals for their Ryzen 8000G processors: Phoenix 1 and Phoenix 2. While Phoenix 1 employs exclusively Zen 4 cores, Phoenix 2 utilises both Zen 4 and the smaller Zen 4C cores. This distinction primarily contributes to increased chip efficiency. As server tests for AMD EPYC processors show, Zen 4C cores perform only slightly worse than standard Zen 4 cores and retain multithreading capabilities.
Gigabyte’s Findings
According to PCGamesN, data from Gigabyte reveals that the differences between Phoenix 1 and Phoenix 2 are more significant than they initially appear. This information was found in the specifications of the Gigabyte B650E Aorus Elite X AX Ice motherboard on the manufacturer’s site.
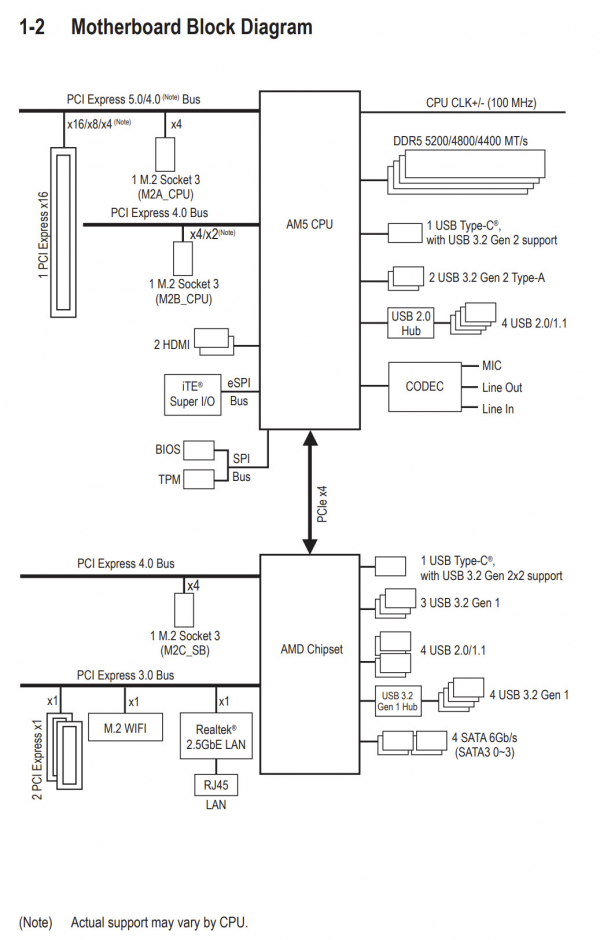
Varying PCIe Support in AMD Chips
Phoenix 2 supports fewer PCIe lanes than Phoenix 1. It supports just two PCIe 4.0 lanes for NVMe solid-state drive (SSD) connectivity via the M.2 slot and four PCIe 4.0 lanes for a discrete graphics card. Phoenix 1, on the other hand, supports eight lanes for the GPU and an SSD with a full PCIe 4.0 x4 interface.
Impact of Fewer PCIe Lanes on GPU Performance
The reduced dedicated lines for the GPU in the Phoenix 2-based Ryzen 5 8500G and Ryzen 3 8300G could potentially lead to decreased graphical performance when used with flagship video cards. It’s worth mentioning that the latter will be distributed by system integrators in pre-assembled computer builds. To avoid potential graphics performance issues, consumers can choose Phoenix 1-based Ryzen 5 8600G and Ryzen 7 8700G processors.